Introduction
The last years electric engines on RIBs and other boats are slowly emerging but what with the hydrogen as fuel? I did some research on the subject and incorporated it into this high-level article.
Hydrogen and electricity have a long history as energy sources, but both have also been gaining increased attention in recent years. Both are seen as potential alternatives to fossil fuels, but their relative advantages and disadvantages need to be considered.
Table of Contents
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the first element on the periodic table, due to its atomic number being one. This means that it has only one electron in its atom. It is also lighter than Helium This has consequences in storing hydrogen.
Hydrogen can be stored in several ways, as a gas or as a liquid. Usually, storing it as gas requires tanks of high pressure ranging from 350 to 700 bar (5,000 to 10,000 psi). As comparison we live in 1 bar.
For liquid hydrogen storage, it must be kept at a temperature at a cryogenic level as the boiling point of hydrogen pressure at 1 atmosphere is -252.8°C. For the sake of completeness, hydrogen can also be stored on solid surfaces via adsorption or within solids by absorption.
Pros and Cons

Hydrogen and electricity each have their pros and cons.
Electricity has the advantage of being much more widely available than hydrogen.
It is relatively easy to transmit and distribute, and can be generated from a variety of sources such as nuclear, solar, wind, and hydropower. Furthermore, it is relatively easy to store and efficient to use.
Problem with batteries is that you need a lot of them to store onboard and with them comes a lot of extra weight. The difference in weight with a combustion engine is huge.
Hydrogen, on the other hand, is much less widely available than electricity. It is difficult to transport, store, and use efficiently, due to its low energy density.
However, H2 is an abundant, renewable, and nearly emissions-free source of energy. When burned or used in a fuel cell, it does not produce massive greenhouse gases and can be used to power vehicles and other applications.
Nearly Emission Free?
When hydrogen is used as fuel, a small amount of oil is burnt whilst using its internals. This can lead to some minor levels of carbon particulate emissions being released into the environment.
For the production a lot of water and energy is needed which impacts the envirornment as well depending on the method used. Producing green hydrogen is the way to go.
Cost of Hydrogen and Electricity
When it comes to cost concerning hydrogen and electricity, electricity is generally the cheaper option.
The cost of generating electricity is relatively low, and the infrastructure for transmitting and distributing it is already in place in many parts of the world.
In contrast, the cost of hydrogen production, storage, and distribution are higher.
Environmental Impact

In terms of environmental impact, both electricity and hydrogen have some advantages and disadvantages.
Electricity generation can produce emissions depending on the source, while hydrogen is emissions-free when burned or used in a fuel cell.
Know that batteries are hugely polluting though this is kept quiet by politicians and lobbyists that promote electricity as the solution for the future.
Batteries contain a number of heavy metals and toxic chemicals and disposing of them by the same process as regular household waste has raised concerns over soil contamination and water pollution (Wikipedia).
To be fair, hydrogen production can generate emissions, depending on the method used but it is here to stay.
An H2 V8 Engine
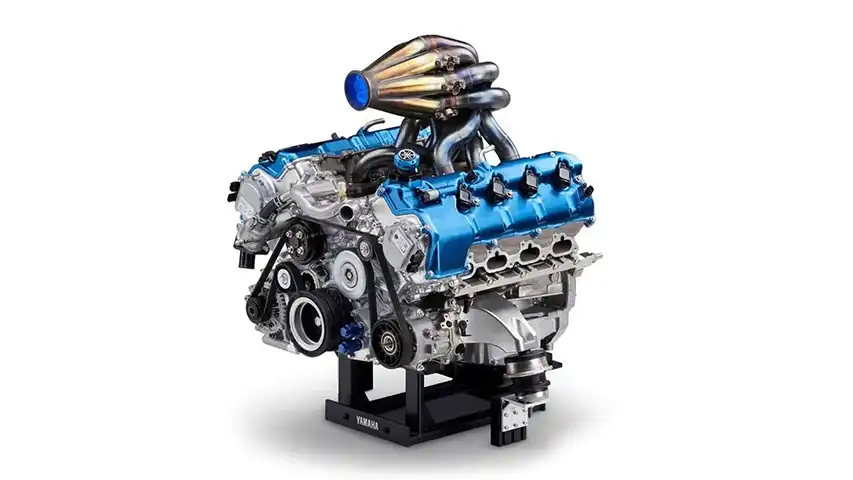

Toyota and Yamaha have united to bring forth an amazing innovation in hydrogen combustion engines, namely a 5.0L V8 engine which has 335 kW of power and 540 Nm of torque, all while emitting extremely low exhaust.
Kawasaki, H2 Japan’s Driving Force
Kawasaki is project leader in a collaboration between Kawasaki, Toyota, Lexus, Yamaha, Mazda and Subaru. Together, they are developing hydrogen engines. The first one ready is a V8 for Lexus.
Kawasaki has very much technological know-how in this matter. Follow Kawasaki Heavy Industries on Facebook and this website to stay updated on towards achieving carbon neutrality.
And what about bio fuel and bio gas? Well, that’s another story.



